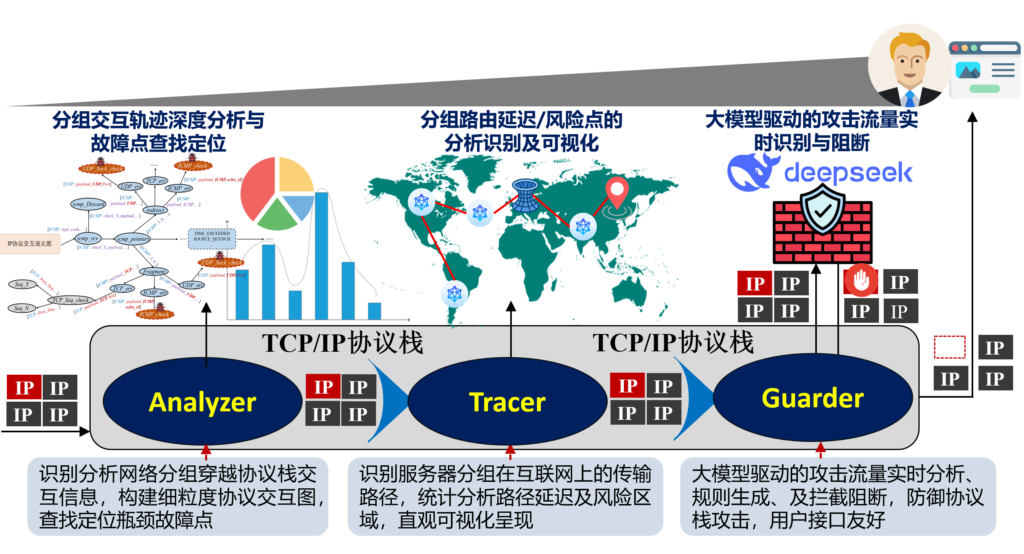
协议栈安全
PacketScope is a general-purpose protocol stack analysis and debugging tool based on eBPF. It integrates performance optimization, anomaly diagnosis, and security defense. It aims to implement fine-grained tracing and intelligent analysis of network packets at the protocol stack level on the server side. By solving three major pain points—difficult diagnosis of performance bottlenecks, unclear transmission paths, and hard-to-detect low-level attacks—PacketScope provides visualized, intelligent endpoint-side security analysis and defense capabilities.
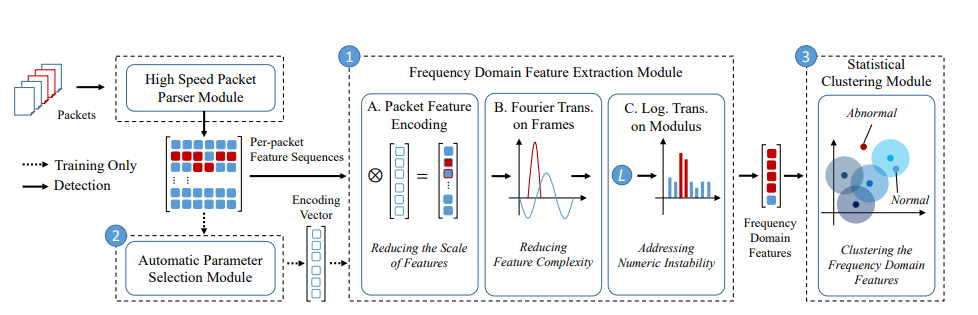
流量检测
Whisper is a real-time malicious traffic detection system based on machine learning. It leverages frequency-domain features to represent sequential traffic information with bounded information loss, ensuring both high detection accuracy and high throughput. By constraining the feature scale, Whisper achieves efficient real-time detection even in high-throughput networks. Compared with traditional rule-based and existing ML-based systems, it is more robust against sophisticated and stealthy evasion attacks. Extensive experiments on 42 attack types demonstrate that Whisper improves AUC by up to 18.36% and achieves two orders of magnitude higher throughput, while maintaining around 90% detection accuracy under various evasion scenarios.
NetBeacon is an intelligent data plane system that integrates machine learning models directly into the network data plane for real-time traffic analysis. It introduces a multi-phase sequential architecture to dynamically analyze packets across different flow stages, leveraging flow-level features computable at line speed to significantly improve accuracy. To ensure efficient deployment, NetBeacon designs compact model representations to mitigate table entry explosion and introduces tightly coupled mechanisms to manage stateful storage for concurrent flows. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that NetBeacon advances both accuracy and scalability for a wide range of traffic analysis tasks.
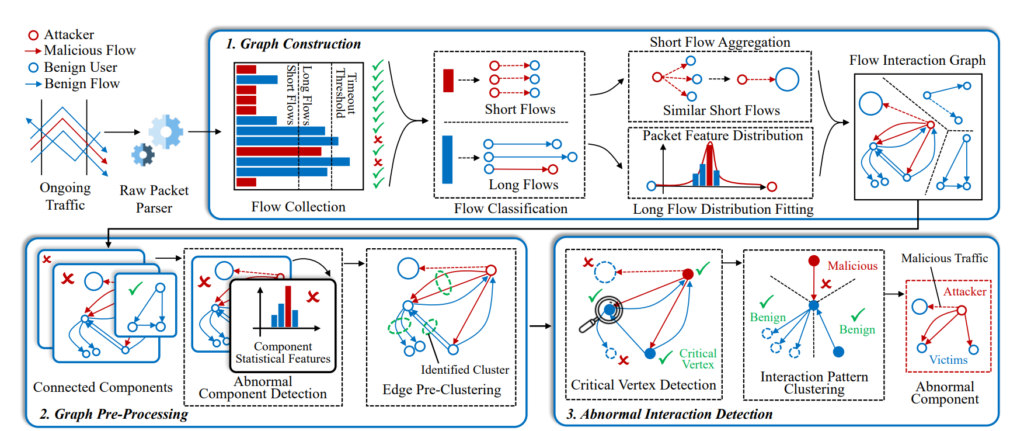
HyperVision is a real-time unsupervised machine learning system for detecting unknown encrypted malicious traffic. Instead of relying on labeled datasets of known attacks, it builds a compact in-memory flow interaction graph that captures structural traffic patterns. By applying unsupervised graph learning on connectivity, sparsity, and statistical features, HyperVision can uncover abnormal interaction patterns that correspond to encrypted attacks. The system achieves high detection robustness against evasive behaviors, reaching AUC ≥ 0.92 and F1 ≥ 0.86 on 92 real-world datasets, while maintaining throughput of at least 80.6 Gb/s with sub-second latency.
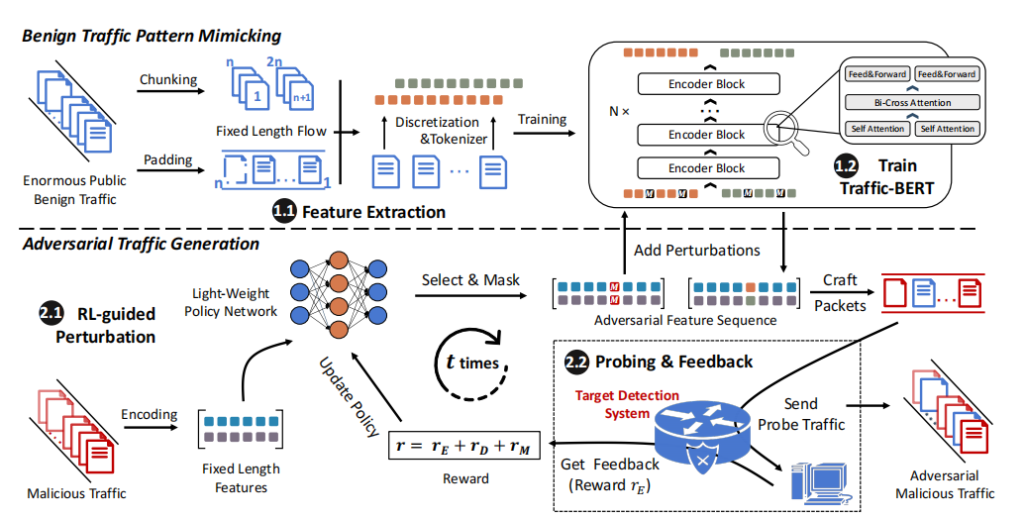
NetMasquerade is a hard-label black-box adversarial attack designed to evaluate the robustness of ML-based malicious traffic detection systems. It is built upon a two-stage framework that first captures benign traffic patterns and then uses them to guide the generation of adversarial traffic. The first stage uses a tailored pre-trained model, Traffic-BERT, to learn diverse benign traffic distributions. The second stage then employs an RL framework to embed these benign traffic patterns into malicious flows with minimal modifications. This method ensures the attack’s efficiency and effectiveness, successfully evading detection while preserving the original malicious functionality.
流量大模型
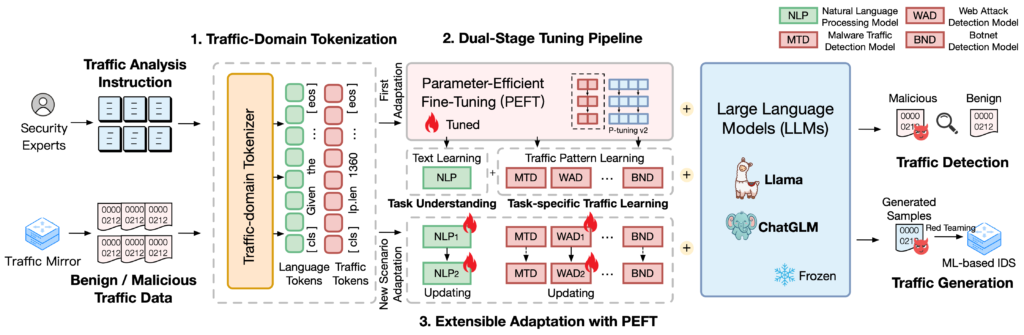
The repository of TrafficLLM is a universal LLM adaptation framework to learn robust traffic representation for all open-sourced LLM in real-world scenarios and enhance the generalization across diverse traffic analysis tasks. TrafficLLM is built upon a sophisticated fine-tuning framework using natural language and traffic data, which proposes the techniques including traffic-domain tokenization, dual-stage tuning pipeline, and extensible adaptation with parameter-effective fine-tuning, to enhance the utility of large language models in network traffic analysis.
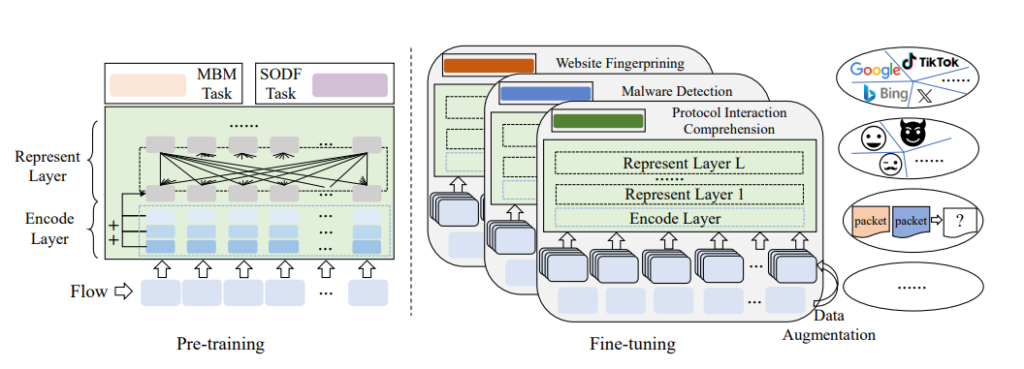
TrafficFormer is a pre-training model designed for network traffic data to address the challenge of limited labeled datasets. In the pre-training stage, it introduces a fine-grained multi-classification task to enhance traffic representation, while in the fine-tuning stage it proposes a traffic data augmentation method that leverages random field initialization to help models focus on key information. Extensive evaluations on traffic classification and protocol understanding tasks show that TrafficFormer improves F1 scores by up to 10% across six datasets and significantly outperforms existing pre-training approaches in protocol understanding.
智能数据面
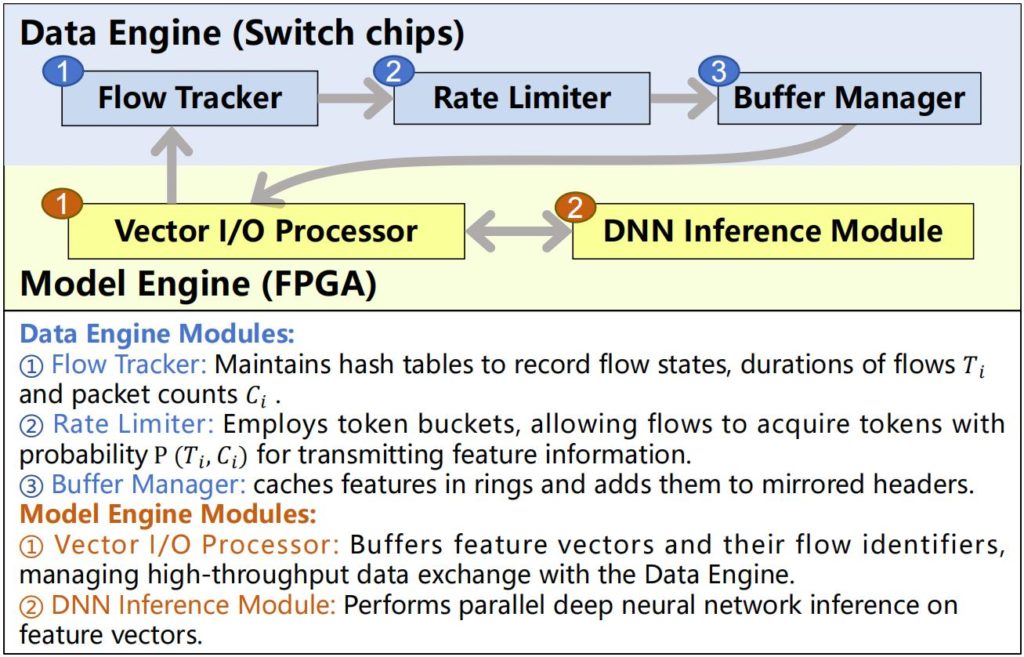
FENIX is a hybrid in-network DNN inference system designed to enable high-accuracy, low-latency traffic analysis on programmable network switches. It is built upon a two-stage architecture that first extracts traffic features on programmable switch ASICs and then performs deep neural network inference on FPGAs. The first stage employs a Data Engine to efficiently extract and cache packet-level features from multi-terabit traffic streams using Flow Tracker, Rate Limiter, and Buffer Manager modules. The second stage then utilizes a Model Engine to execute complex neural networks directly in the data plane with microsecond-level latency. This method ensures the system’s scalability and practicality, successfully achieving high classification accuracy on encrypted traffic and malware detection while maintaining multi-terabit throughput.
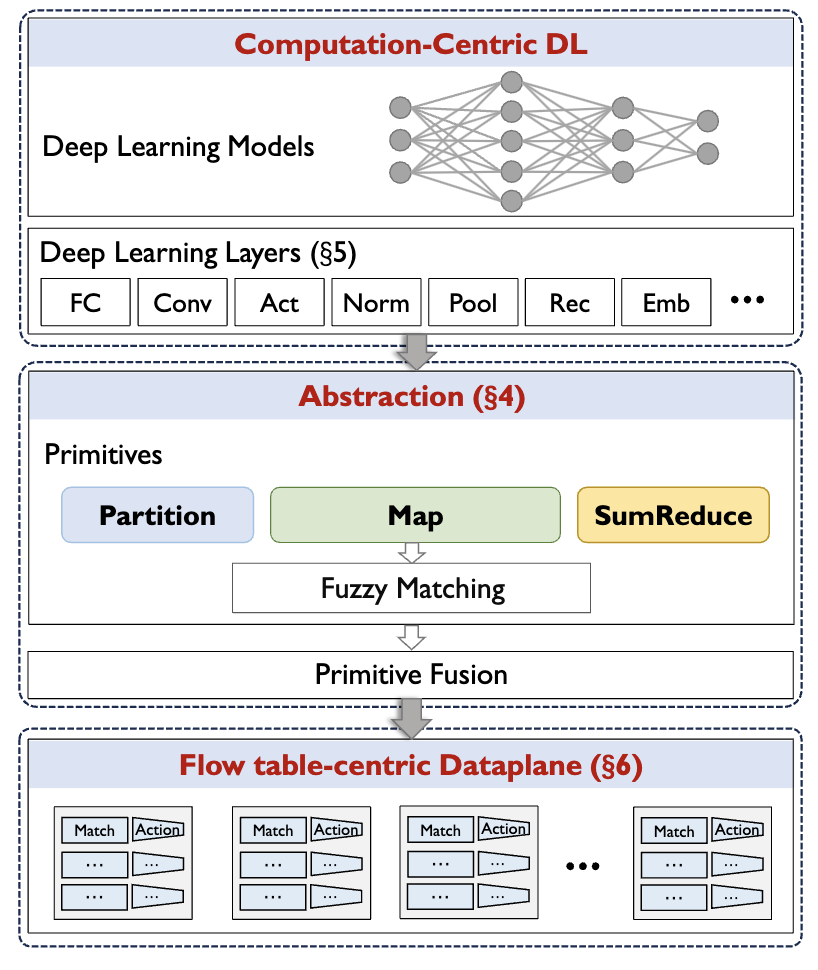
Pegasus is a universal DNN-inference framework for programmable data planes that compiles models into three primitives—Partition. Map and SumReduce—to run on P4 switches. It uses fuzzy-matching indices and primitive fusion to shrink tables and pipeline cost, and combines full-precision weights with fixed-point activations and a safe aggregation layout. The result is consistent software–hardware outputs, support for multiple model families (MLP/RNN/CNN/AE), and line-rate, nanosecond-scale execution on constrained dataplanes.
课程材料
This course focuses on the disciplinary framework of cyberspace security, with an emphasis on introducing the fundamental theories, issues, and mechanisms related to the field. It aims to familiarize students with the overall structure of cyberspace security, provide them with a systematic understanding of its foundational knowledge, raise awareness of potential security risks, and strengthen their security consciousness. The course covers a range of topics, including basic theories, mechanisms, and algorithms of cyberspace security, applied cryptography, system security, network security, application security, and data security. In addition, typical security incidents and case studies are incorporated to inspire critical thinking, enabling students to acquire preliminary skills in analyzing and preventing security problems. Representative laboratory experiments are also designed to deepen students’ understanding of cyberspace security issues.